I still remember the first time I decided to try the ketogenic lifestyle. The idea of switching my body’s primary fuel source from carbs to fat felt like a challenge, but I was determined to make it work. Like many beginners, I wondered how to get into keto the right way without feeling overwhelmed.
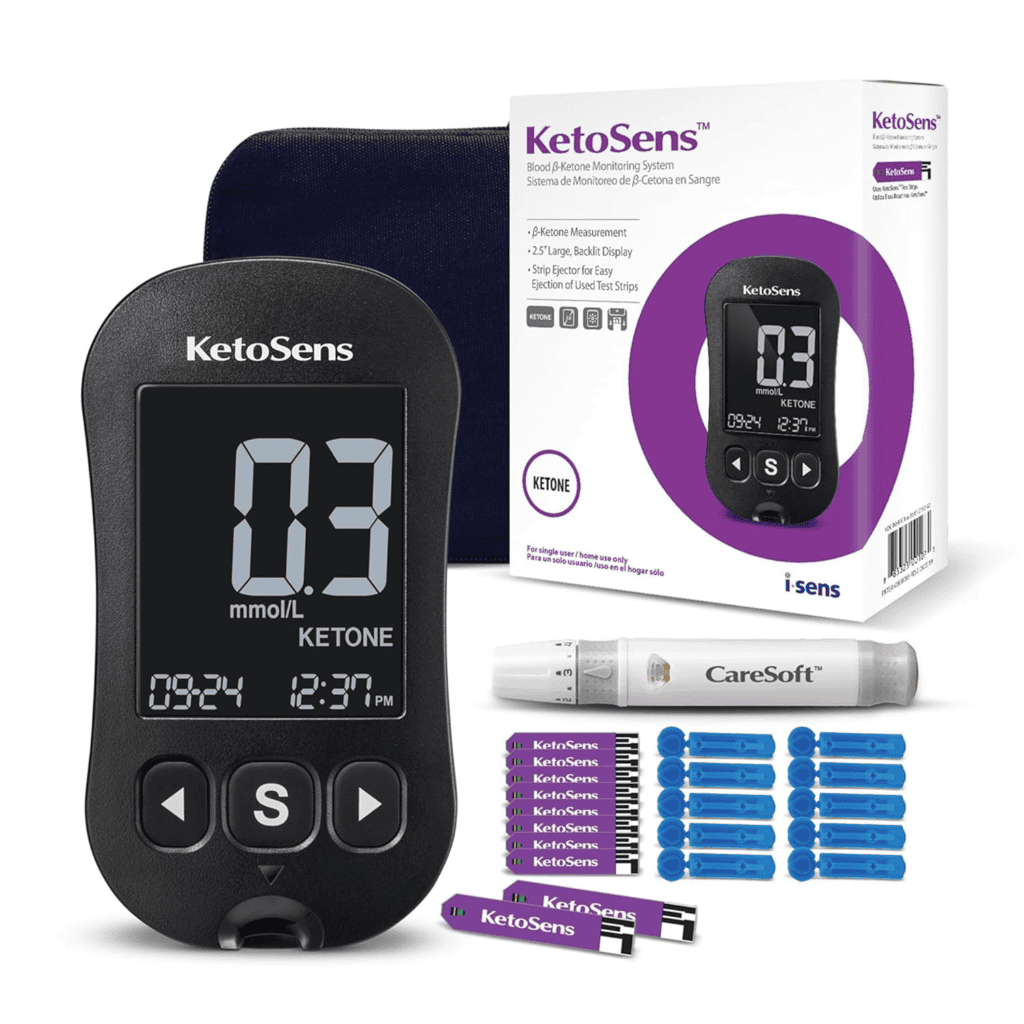
Through trial, error, and a lot of research, I discovered that success starts with the right tools—especially tracking ketone levels to ensure you’re in ketosis. One of the best ways to do this is with the KetoSens Blood Ketone Monitoring Starter Kit, which provides accurate readings to help you stay on track.
This article contains affiliate links, meaning I may earn a commission if you click and make a purchase at no additional cost to you. As an affiliate, I only recommend products or services I believe will add value to my readers. Your support helps keep this site running. Thank you!
If you’re ready to dive into keto, let’s break down the science, strategies, and practical tips to help you succeed.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet fundamentally shifts your body’s primary fuel source from glucose to ketones. This metabolic state, known as ketosis, occurs when you drastically reduce carbohydrate intake and increase consumption of healthy fats.
A standard ketogenic diet typically follows a macronutrient ratio of:
- 70-75% fat
- 20-25% protein
- 5-10% carbohydrates
The Science Behind Ketosis
On a high-carbohydrate diet, your body primarily uses glucose for energy. However, when carbohydrate intake is severely restricted, your liver begins converting fatty acids into ketone bodies.
These ketones then become the primary fuel source for your brain and body.
This metabolic shift can lead to several potential benefits:
- Increased fat burning
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Enhanced mental clarity and focus
- Reduced inflammation
- Potential neuroprotective effects
Getting Started with Keto
Transitioning to a ketogenic diet needs careful planning and preparation. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you begin:
1. Calculate Your Macros
The first step is determining your daily calorie needs and breaking them down into suitable macronutrient ratios. Use my online macro calculator to help you with this process.

Remember, these are starting points, and you may need to adjust based on your personal response to the diet.
2. Clean Out Your Pantry
Remove high-carb foods from your kitchen and stock up on keto-friendly options. This includes:
- Meats and fatty fish
- Eggs
- Low-carb vegetables (leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini)
- Nuts and seeds
- Healthy oils (olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil)
- Full-fat dairy products (if tolerated)
3. Plan Your Meals
Create a meal plan that adheres to your macronutrient goals. Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods to confirm you’re getting adequate vitamins and minerals.
Some popular keto meals include:
- Bacon and eggs with avocado
- Grilled salmon with asparagus and hollandaise sauce
- Cauliflower rice stir-fry with chicken and vegetables
- Keto chili made with ground beef and low-carb vegetables
4. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is crucial when starting a ketogenic diet. Drink plenty of water and consider supplementing with electrolytes to prevent dehydration and minimize keto flu symptoms.
5. Track Your Progress
Use a food tracking app to watch your macronutrient intake. Consider using ketone testing methods (blood, urine, or breath) to confirm you’re in ketosis.
Navigating Potential Challenges
As you begin your keto diet, be prepared for some potential hurdles:
Keto Flu
Many people experience flu-like symptoms when first starting keto, including fatigue, headaches, and irritability. This is typically temporary and can be managed with proper hydration, electrolyte supplementation, and gradually reducing carbohydrate intake.
Ultima Replenisher Daily Electrolyte Hydration mix provides a blend of essential minerals to keep you hydrated and energized.
Social Situations
Eating out or attending social gatherings can be challenging on a ketogenic diet. Plan ahead by researching keto-friendly options at restaurants, bringing your own dishes to potlucks, and communicating your dietary needs to friends and family.
Nutrient Deficiencies
A poorly planned keto diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies. Focus on incorporating a variety of foods and consider supplementation if necessary.
Pay particular attention to:
- Magnesium
- Potassium
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Fiber
Adherence
Sticking to such a low carb intake can be difficult for some people. Consider starting with a less restrictive low-carb diet and gradually transitioning to full keto.
Remember, consistency is key, and it’s okay to have occasional higher-carb days if it helps you maintain the diet long-term.
Advanced Keto Strategies
Once you’ve mastered the basics of keto, you may want to explore more advanced strategies:
Intermittent Fasting
Combining keto with intermittent fasting can potentially enhance fat burning and ketone production. Common fasting protocols include:
- 16/8 method (16 hours fasting, 8-hour eating window)
- 24-hour fasts (once or twice a week)
- 5:2 diet (eating normally for 5 days, restricting calories for 2 non-consecutive days)
Cyclical Keto Diet
This approach involves following a standard keto diet for 5-6 days, followed by 1-2 days of higher carb intake. This can be useful for athletes or those who find strict keto challenging to maintain long-term.
Targeted Keto Diet
This variation allows for extra carbohydrates around workouts. It’s designed for athletes and highly active people who need extra glucose for high-intensity performance.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Keto Diet
As you progress on your keto diet, it’s important to watch your progress and make adjustments as needed:
- Regularly check your ketone levels using blood, urine, or breath tests.
- Track your weight, body measurements, and progress photos.
- Pay attention to how you feel – energy levels, mental clarity, and overall well-being.
- Adjust your macros if you’re not seeing the desired results or experiencing negative side effects.
- Consider periodic carb refeeds if you’re very active or have been on keto for an extended period.
Regularly checking your ketone levels is essential to ensure you’re in ketosis. The KetoSens Blood Ketone Monitoring Starter Kit offers accurate readings and syncs seamlessly with a free app for comprehensive tracking.
Check your ketone levels with the KetoSens Blood Ketone Monitoring Starter Kit
Cyclical Keto Diet
This approach involves following a standard keto diet for 5-6 days, followed by 1-2 days of higher carb intake. This can be useful for athletes or those who find strict keto challenging to maintain long-term.
Targeted Keto Diet
This variation allows for extra carbohydrates around workouts. It’s designed for athletes and highly active people who need extra glucose for high-intensity performance.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Keto Diet
As you progress on your keto diet, it’s important to watch your progress and make adjustments as needed:
- Regularly check your ketone levels using blood, urine, or breath tests.
- Track your weight, body measurements, and progress photos.
- Pay attention to how you feel – energy levels, mental clarity, and overall well-being.
- Please consider adjusting your macros if you are not achieving the desired results or are experiencing negative side effects.
- Consider periodic carb refeeds if you’re very active or have been on keto for an extended period.
Keto for Specific Health Goals
While fat loss is a common goal for those starting keto, the diet may have extra health benefits:
Diabetes Management
Keto can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, the diet helps stabilize blood glucose levels and may reduce the need for diabetes medications in some people.
However, it’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider when making significant dietary changes, especially if you’re taking diabetes medications.
Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet was originally developed as a treatment for epilepsy, particularly in children who didn’t respond well to anti-seizure medications. The high-fat, low-carb approach alters brain chemistry in a way that can reduce seizure frequency and severity in some patients.
While it’s not effective for everyone, many people with epilepsy have found significant relief through a ketogenic diet.
Mental Clarity
Many people report improved focus and cognitive function on keto. This could be because of the brain’s effective use of ketones for fuel, as well as the stabilization of blood sugar levels.
Some studies suggest that ketones may have neuroprotective properties, potentially benefiting conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Cardiovascular Health
Contrary to initial concerns about a high-fat diet, research suggests that a well-formulated ketogenic diet may actually improve cardiovascular health markers. Many people experience improvements in their cholesterol profiles, with increases in HDL (good) cholesterol and decreases in triglycerides.
The diet may also help reduce inflammation, a key factor in heart disease.
Practical Tips for Long-Term Keto Success
Meal Prep and Planning
One of the keys to success on a ketogenic diet is preparation. Spend some time each week planning your meals and snacks.
This helps confirm you always have keto-friendly options on hand and reduces the temptation to reach for high-carb convenience foods.
Some meal prep ideas include:
- Hard-boiling a dozen eggs for quick snacks or salad toppings
- Preparing a large batch of cauliflower rice to use throughout the week
- Cooking a whole chicken to use in various meals
- Making a big pot of keto-friendly soup or chili
Keto-Friendly Snacks
Having a variety of keto-friendly snacks readily available can help you stay on track, especially when cravings hit. Quest Nutrition Tortilla Style Protein Chips offer a crunchy, low-carb option.
>>> Enjoy a tasty snack with Quest Nutrition Protein Chips <<<
Some other options are:
- Nuts and seeds (in moderation)
- Cheese sticks
- Olives
- Pork rinds
- Beef jerky (check for added sugars)
- Avocado
- Celery sticks with almond butter
Eating Out on Keto
Dining out doesn’t have to derail your keto diet. Most restaurants offer options that can be easily modified to fit your macros.
Some strategies include:
- Ordering burgers without the bun
- Choosing grilled meats or fish with low-carb vegetable sides
- Opting for salads with high-fat dressings (watch out for hidden carbs in dressings)
- Asking for substitutions (e.g., extra vegetables instead of potatoes)
Dealing with Cravings
Cravings for high-carb foods are common, especially in the early stages of keto. Here are some ways to manage them:
- Stay hydrated – sometimes thirst can be mistaken for hunger
- Eat enough fat – it helps keep you satiated
- Try keto-friendly versions of your favorite foods (e.g., cauliflower pizza crust)
- Distract yourself with activities unrelated to food
- Get enough sleep – lack of sleep can increase cravings
Supplementation on Keto
While a well-formulated ketogenic diet can provide most necessary nutrients, some people may benefit from supplementation. Common supplements for keto dieters include:
- Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium)
- MCT oil – for an extra boost of easily digestible fats
- Omega-3 fatty acids – especially if not consuming much fatty fish
- Vitamin D – particularly important if you don’t get much sun exposure
- Fiber supplements – if struggling to get enough from low-carb vegetables
Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are fats that are rapidly absorbed and converted into energy, supporting ketosis. Nature’s Way Organic MCT Oil is a popular choice among keto dieters.
Boost your energy with Nature’s Way Organic MCT Oil, check the price HERE.
Overall health
While the keto diet is primarily focused on nutrition, overall health is best supported with a holistic approach. Incorporating tools that aid in recovery and stress reduction can significantly enhance your wellness journey. For instance, Massage Chairs and their Health Benefits are often overlooked but can play a crucial role in reducing inflammation, improving circulation, and promoting better sleep — all important factors during keto adaptation.
Exercise on a Ketogenic Diet
Contrary to what a lot of people believe, you can maintain an active lifestyle while following a ketogenic diet. However, you may need to make some adjustments, especially during the initial adaptation period.
Aerobic Exercise
Many people find their endurance improves on a ketogenic diet once they’re fully fat-adapted. This is because the body becomes more effective at using fat for fuel during low to moderate-intensity activities.
Strength Training
Strength training can be maintained on a ketogenic diet, but you might experience a temporary decrease in performance during the adaptation phase. Some people find they need to slightly increase their carb intake around workouts to maintain intensity.
High-Intensity Exercise
High-intensity activities may be more challenging on a strict ketogenic diet, as these rely heavily on glycogen stores. Some athletes choose to follow a targeted or cyclical ketogenic diet to support their high-intensity training.
Keto for Special Populations
Keto for Women
Women may need to approach the ketogenic diet differently than men because of hormonal considerations. Some women find they need slightly higher carb intake or more frequent carb cycling to maintain hormonal balance and menstrual regularity.
Keto for Vegetarians and Vegans
While more challenging, it’s possible to follow a ketogenic diet as a vegetarian or vegan. Key protein sources include:
- Eggs and dairy (for vegetarians)
- Tofu and tempeh
- Seitan (wheat gluten)
- Nuts and seeds
- Plant-based protein powders
Vegan keto dieters need to pay extra attention to getting enough complete proteins and may need to supplement with vitamin B12 and omega-3 fatty acids.
Keto for Older Adults
Older adults may benefit from a ketogenic diet, particularly for brain health and metabolic improvements. However, it’s crucial to confirm adequate protein intake to prevent muscle loss.
Working with a healthcare provider is especially important for this population.
Common Keto Mistakes to Avoid
- Not getting enough electrolytes
- Eating too much protein
- Not eating enough fat
- Obsessing over ketone levels
- Neglecting fiber intake
- Not giving your body time to adapt
- Failing to plan ahead
The Future of Keto Research
The ketogenic diet continues to be an area of active research. Some exciting areas of study include:
- Keto’s potential role in cancer treatment
- The long-term effects of ketogenic diets on cardiovascular health
- The impact of keto on gut microbiome composition
- Ketogenic diets as a potential treatment for neurodegenerative diseases
- The effects of keto on athletic performance and recovery
As research progresses, we may gain even more insights into the potential benefits and applications of ketogenic diets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ketosis?
Ketosis is a metabolic state where your body primarily uses fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates. This occurs when carbohydrate intake is very low, typically below 50 grams per day for most people.
How long does it take to get into ketosis?
The time it takes to enter ketosis can vary from person to person, but it typically occurs within 2-4 days of drastically reducing carbohydrate intake. Some people may take up to a week or more.
Can I drink alcohol on a keto diet?
Some alcoholic beverages can fit into a ketogenic diet in moderation. Hard liquors like vodka, gin, and whiskey contain zero carbs.
However, beer, wine, and mixed drinks often contain significant amounts of carbs and should be limited or avoided.
Is the keto diet safe for everyone?
While many people can safely follow a ketogenic diet, it’s not suitable for everyone. People with certain medical conditions, such as pancreatitis, liver failure, or disorders of fat metabolism, should avoid keto.
Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new diet.
How much weight can I expect to lose on keto?
Weight loss varies greatly from person to person. Some people may experience rapid initial fat loss, especially water weight, in the first week or two.
After that, a more gradual fat loss of 1-2 pounds per week is common.
Can I eat fruit on a keto diet?
Most fruits are high in carbs and should be limited on a ketogenic diet. However, small amounts of low-carb fruits like berries can often be incorporated in moderation.
Is the keto diet good for building muscle?
Building muscle on a ketogenic diet is possible, but it may need careful planning to confirm adequate protein intake without exceeding carb limits. Some people find they need to change the diet (e.g., targeted keto) to support muscle growth effectively.
How do I know if I’m in ketosis?
Common signs of ketosis include decreased hunger, increased energy and mental clarity, and a fruity or metallic taste in the mouth. However, the most accurate way to confirm ketosis is through blood, urine, or breath testing for ketones.
Can the keto diet help with acne?
Some people report improvements in acne while following a ketogenic diet. This may be because of reduced inflammation and stabilized blood sugar levels.
However, person results can vary.
Is keto safe during pregnancy?
The safety of a ketogenic diet during pregnancy is not well-established. Pregnant women should talk to their healthcare provider before making any significant dietary changes.
Key Takeaways
- The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carb approach that shifts your body’s primary fuel source from glucose to ketones.
- Proper planning and preparation are crucial for successfully transitioning to a keto diet.
- Be prepared for potential challenges like the keto flu and navigating social situations.
- Advanced strategies like intermittent fasting can enhance the benefits of keto.
- Regular monitoring and adjustments are necessary for long-term success on keto.